CWD Hunting Regulations & Carcass Transportation Restrictions
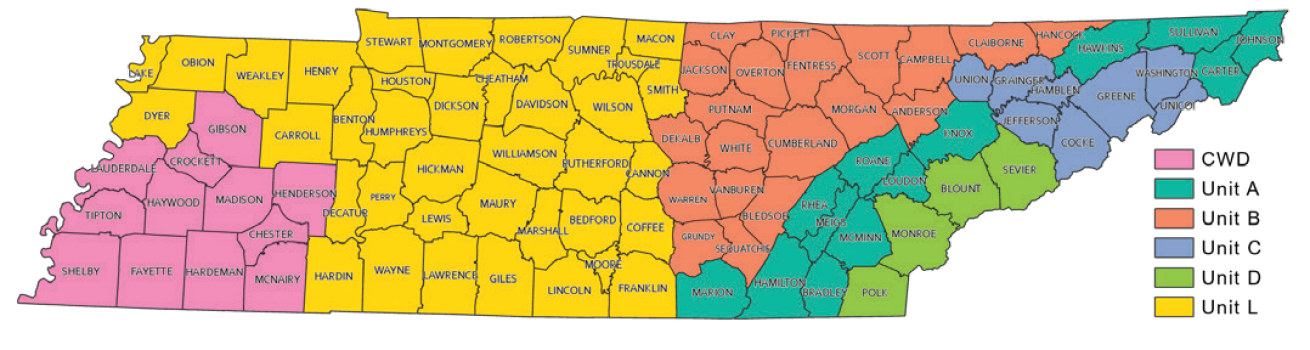
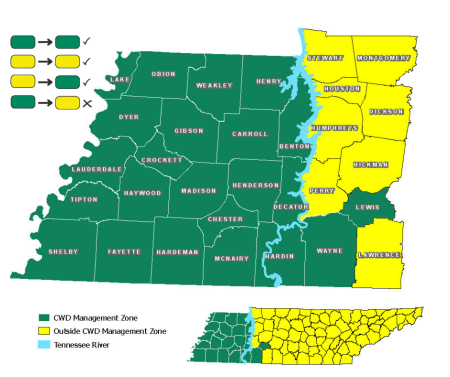
Unit CWD counties have not changed from last season and include Chester, Crockett, Fayette, Gibson, Hardeman, Haywood, Henderson, Lauderdale, Madison, McNairy, Shelby, and Tipton counties. CWD Positive counties outside of Unit CWD (Benton, Carroll, Decatur, Dyer, Hardin, Henry, Lake, Lewis, Wayne, and Weakley counties) are in Unit L for hunting regulations but must still follow CWD carcass transportation and feeding restrictions.
If a county becomes CWD-positive, ONLY carcass transport restrictions and wildlife feeding restrictions immediately go into effect. Other Unit CWD regulations including methods of take and deer season dates, however, do NOT automatically go into effect. These changes require action by the Tennessee Fish & Wildlife Commission. Check out this Deer Hunting Unit map to know which Unit you will be hunting in.
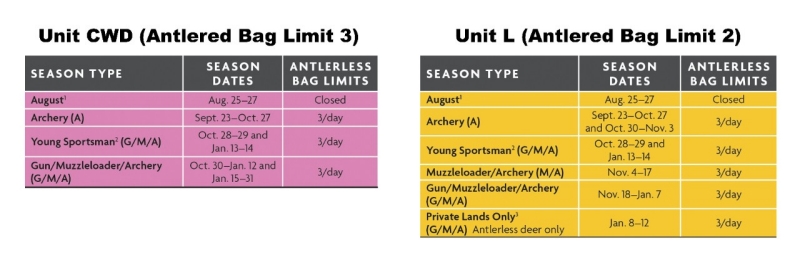
1. Private lands only and archery only, except in Unit CWD where guns and muzzleloaders are allowed and select public lands are additionally open for hunting. See Region 1 WMA regulations starting on page 49 to see which public lands are open during this hunt. Fluorescent orange is required in Unit CWD.
2. Youths 6-16 years of age may participate. Participating youth can use guns, muzzleloaders, and archery equipment (G/M/A). Young sportsmen must be accompanied by a non-hunting adult, 21 years of age or older, who must remain in a position to take immediate control of the hunting device and who must also comply with fluorescent orange regulations, as specified for legal hunters. Multiple youths may be accompanied by a single, qualifying adult. Antlerless bag limits for Units A, B, C, and D are not to exceed a total of 2 antlerless deer for the four days combined.
3. Hunting is allowed on all privately owned lands in Unit L (including leased land and lands owned by individuals). It is the responsibility of all hunters to obtain verbal or written permission to hunt on privately owned lands. No public lands or WMAs are open during this period. No antlered deer may be taken during this period in Unit L.
Carcass Transportation Restrictions
Carcass transport restrictions, along with wildlife feeding and mineral placement restrictions, are immediately triggered when a county becomes CWD positive.
Please note that Benton, Carroll, Decatur, Dyer, Hardin, Henry, Lake, Lewis, Wayne, and Weakley Counties are in deer Unit L, not Unit CWD, and must still follow these transport regulations.
Once any unapproved deer part is taken into a positive county, it must remain in positive counties.
Deer harvested in counties that are not affected by CWD do not have to meet carcass restrictions to be transported into CWD affected counties.
Deer carcass transportation and wildlife feeding restrictions apply to the CWD Management Zone. Therefore, if a new county becomes positive (based on CWD test results) these restrictions will automatically apply.
- Do not move whole or field-dressed deer carcasses or unapproved parts outside of CWD affected counties. Only approved parts (listed below) may be moved out of CWD affected counties.
- Deer carcasses can move within and between counties in the CWD Management Zone.
- Once a carcass is brought into the CWD Management Zone, it cannot be moved out of the zone.
- Approved parts (listed below) are free to be transported anywhere statewide.
- Also remember, only Approved Parts can be transported into Tennessee from another state.
Wildlife Feeding Restrictions Within CWD Management Zone
Within the CWD Management Zone the placement of grain, salt products, minerals, and other consumable natural and manufactured products is prohibited.
Feeding restrictions do not apply if the feed or minerals are:
- placed within one hundred (100) feet of any residence or occupied building; or
- placed in such a manner to reasonably exclude access by deer; or
- placed as part of a wild hog management effort authorized by the agency; or
- present from normal agricultural practices, normal forest management practices, or crop and wildlife food production practices.
Approved Parts
These parts have a low risk of spreading CWD.
- Deboned meat
- Antlers, antlers attached to cleaned skull plates, cleaned skulls (where no meat or tissues are attached to the skull)
- Cleaned teeth
- Finished taxidermy and antler products
- Hides and tanned products
Examples of Unapproved Parts
These parts have a high risk of spreading CWD.
- Whole and field-dressed carcasses
- Organs
- Guts
- Uncleaned (meat and/or tissue are present) heads/skulls/skull caps
- Non-muscle tissues
Urine Lure Restriction
The use or possession of natural cervid urine while hunting is prohibited unless the product is clearly labeled bearing certification from the manufacturer that the urine was produced in a facility that:
- Complies with a federal or a federally approved chronic wasting disease herd certification program and any federal chronic wasting disease protocols and record requirements;
- Does not allow the importation of live cervids;
- Requires that all cervids exported from the facility be tested for chronic wasting disease upon death and the results are reported to the facility;
- Is inspected annually by an accredited veterinarian, including inspection of the herd and applicable records; and
- Maintains a fence at least 8 feet high around the facility and, if the facility is located within 30 miles of a confirmed positive occurrence of chronic wasting disease, is double fenced to prevent direct contact between captive and wild cervids.
- Requires an accredited veterinarian to conduct a 100% herd inspection at a minimum of every 3 years: and
- Prior to distribution, tests each lot/batch of cervid collected urine used in a scent product via the Real Time Quaking Induced Conversion (RT-QulC) assay for the presence of Chronic Wasting disease prions.
Important Safety Guidelines
Limit Your Exposure to CWD
There is no scientific evidence that CWD can be naturally transmitted to humans. However, as a general precaution, TWRA and health officials advise that hunters take the following common-sense precautions when handling and processing deer or elk in areas known to have CWD.
- Avoid sick animals. Do not shoot, handle, or consume any animal that appears sick; contact your local wildlife agency personnel.
- Have your animal processed in the area in which it was harvested so high-risk parts can be disposed of properly.
- Wear rubber/latex gloves when field-dressing carcasses.
- Minimize handling of the brain, spinal cord, eyes, spleen, tonsils, and lymph nodes of any deer or elk. Normal field dressing coupled with boning out a carcass will remove most, if not all, of these body parts. Cutting away all fatty tissue will remove the remaining lymph nodes.
- Thoroughly wash hands. Knives and other tools should be washed with warm soapy water to completely remove all visible debris and fat/grease before sanitizing. Sanitize tools by soaking them in a solution of 50 percent household bleach with 50 percent water for 20 minutes. Thoroughly rinse the bleach off. Let air dry.
- While transporting, store all portions of the animal in a container such as a cooler, bin, or bag that will not leak fluids into the environment.
- In CWD affected counties, have your animal tested and do not consume animals that test positive for CWD.
Read more about preventing exposure to CWD through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CWD webpage.